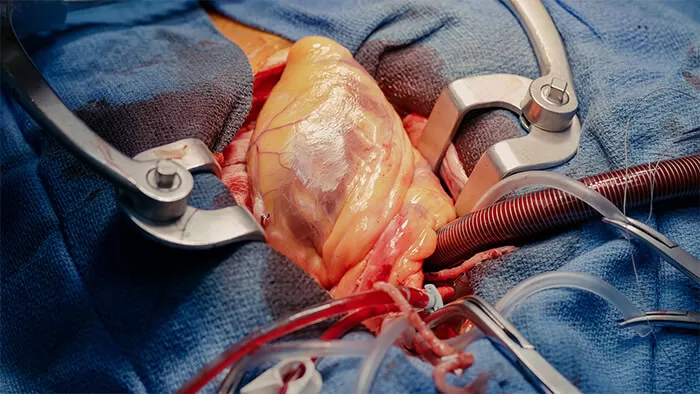
Learn About Cardiothoracic Surgeons: The Heart and Lung Heroes
Introduction
Cardiothoracic surgeons are the unsung heroes of the medical world, specializing in the surgical treatment of conditions related to the heart, lungs, and other vital structures within the chest. In this article, we will delve into the fascinating world of cardiothoracic surgeons, exploring their education, roles, and the crucial contributions they make to healthcare.
The Path to Becoming a Cardiothoracic Surgeon
Becoming a cardiothoracic surgeon is a rigorous and challenging journey that requires unwavering dedication. Let’s break down the steps involved:
1. Pre-Medical Education
Before embarking on the path to becoming a cardiothoracic surgeon, aspiring medical professionals must complete a bachelor’s degree, ensuring they meet the prerequisites for medical school.
2. Medical School
The next step is medical school, a grueling four-year program that provides the foundational knowledge and skills required for a career in medicine.
3. General Surgery Residency
After medical school, individuals interested in cardiothoracic surgery typically enter a general surgery residency program. This phase lasts five to seven years and offers a comprehensive surgical foundation.
4. Cardiothoracic Surgery Fellowship
Following the general surgery residency, a cardiothoracic surgery fellowship follows, lasting an additional two to three years. During this specialized training, surgeons gain expertise in heart and lung surgery.
Roles and Responsibilities
Cardiothoracic surgeons play a pivotal role in the field of medicine, with responsibilities that include:
1. Open-heart Surgery
Cardiothoracic surgeons are renowned for their expertise in open-heart surgery. They perform intricate procedures to repair or replace heart valves, treat congenital heart defects, and conduct coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) to address blocked or narrowed arteries.
2. Lung Surgery
In the realm of lung surgery, cardiothoracic surgeons address conditions such as lung cancer, emphysema, and lung infections. Surgeries like lobectomy, pneumonectomy, and lung volume reduction are carried out to treat these ailments.
3. Heart Transplants
Cardiothoracic surgeons are key players in heart transplant surgeries, where they replace a failing heart with a healthy donor heart. They oversee the transplantation procedure and post-operative care.
4. Minimally Invasive Procedures
Advancements in medical technology have enabled cardiothoracic surgeons to perform minimally invasive procedures. Techniques such as robotic-assisted surgery and video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery (VATS) allow for smaller incisions and quicker recoveries.
5. Vascular Surgery
Some cardiothoracic surgeons also delve into vascular surgery, addressing conditions like aortic aneurysms, peripheral artery disease, and carotid artery disease.
The Impact on Healthcare
Cardiothoracic surgeons hold a critical place in healthcare due to their ability to treat life-threatening and complex conditions of the heart and lungs. Heart disease remains one of the leading causes of mortality worldwide, making their expertise invaluable. Cardiothoracic surgeons collaborate closely with other medical professionals, including cardiologists and pulmonologists, to provide comprehensive care to patients.
In addition to their surgical skills, these surgeons must possess strong communication and interpersonal skills. They work closely with patients and their families, offering guidance and support throughout the treatment process.
FAQs
1. How long does it take to become a cardiothoracic surgeon?
Becoming a cardiothoracic surgeon typically involves four years of medical school, followed by a five to seven-year general surgery residency and a two to three-year cardiothoracic surgery fellowship.
2. What are some common heart conditions treated by cardiothoracic surgeons?
Cardiothoracic surgeons treat a wide range of heart conditions, including coronary artery disease, heart valve disorders, and congenital heart defects.
3. Are there alternatives to open-heart surgery?
Yes, cardiothoracic surgeons can perform minimally invasive procedures, which involve smaller incisions and shorter recovery times. These are suitable for certain heart conditions.
4. What is the success rate of heart transplants?
Heart transplants have a high success rate, with most recipients experiencing improved quality of life and extended survival.
5. Do cardiothoracic surgeons only work on adults, or do they treat pediatric patients as well?
Some cardiothoracic surgeons specialize in pediatric cardiothoracic surgery, addressing heart and lung conditions in children.